From Wikipedia to HubSpot: tracking the hidden power of AI Traffic
Do you have a Wikipedia page?
If your brand isn’t on it yet, you’re missing a major signal in the new search landscape, not just for SEO, but for GEO (Generative Engine Optimization).
The silent power of Wikipedia
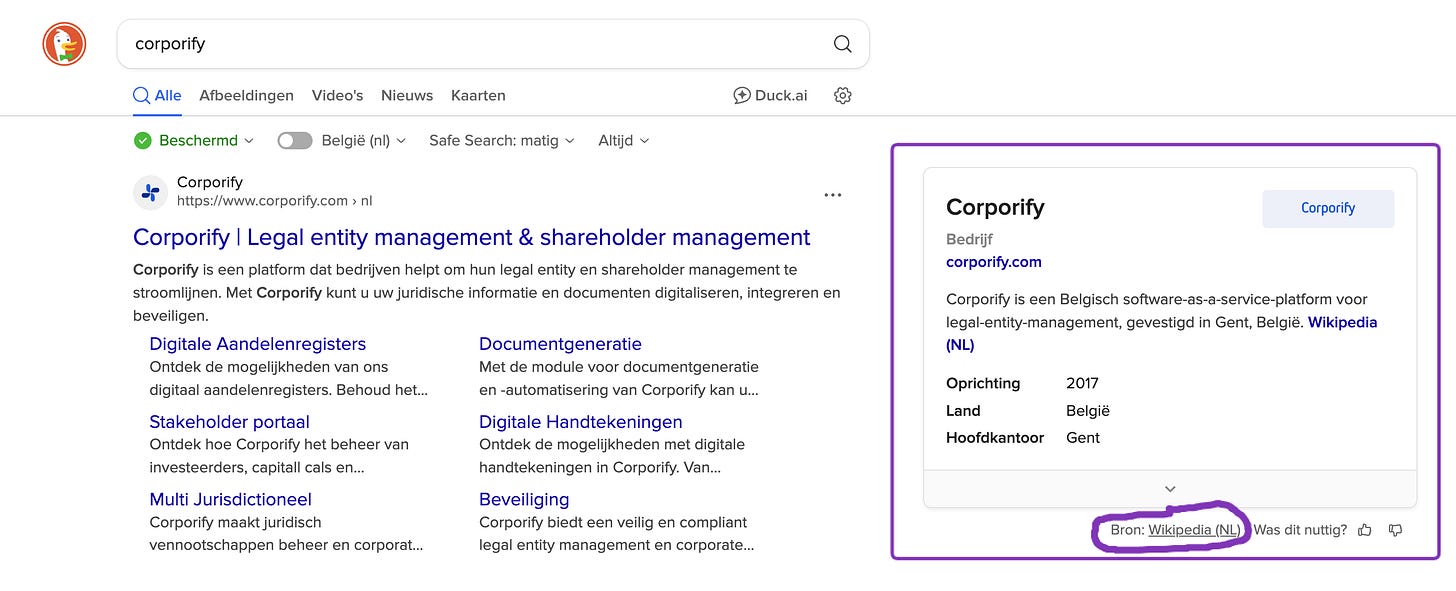
Wikipedia isn’t just another backlink.
It’s just another website, yet AI gives it more authority than most.
When you ask ChatGPT, Claude, or Google AI a question about a company, guess where they often pull data from?
Right: Wikipedia and Wikidata.
LLMs (large language models) treat it as a “trusted truth layer.”
Having a Wikipedia page means your brand story lives inside the data AI tools use to answer questions.
That means:
Your brand becomes more likely to appear in AI-generated summaries.
Your content feeds directly into Google’s Knowledge Graph, improving your entity authority and E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust).
You’re not just improving SEO anymore.
You’re teaching AI who you are.
Google Knowledge Panels
A Wikipedia page isn’t just about visibility.
It’s a credibility anchor.
Imagine a prospect comparing two similar software companies.
One has a well-written Wikipedia page that appears when they Google the brand name. The other doesn’t.
Which one feels more established?
Exactly.
Attribution in HubSpot: AI traffic
Let’s connect the dots to something every growth marketer cares about: attribution.
AI tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Copilot are increasingly driving invisible traffic to websites.
But HubSpot (and most analytics tools) often don’t recognize it, tagging it often as “Direct Traffic.”
That means your AI-driven visitors, the ones who found you through Wikipedia or AI citations, go uncredited.
At Astra+, we tested this by updating HubSpot’s tracking setup.
We did the following:
Add this open text form field: “How did you hear about us?”
Use a HubSpot workflow to group open responses like “ChatGPT,” “Claude,” “AI,” or “Perplexity” under “AI Referrals.” You can use the HubSpot Breeze AI model to interpret the answers and categorise them correctly.
This gives you a clearer picture of how AI-generated visibility converts into pipeline.
The result?
A surprising number of leads that previously looked like “Direct Traffic” were in fact coming from AI-driven mentions.
The growth takeaway
Wikipedia is no longer just an encyclopedia, it’s the API for credibility in the AI era.
It feeds everything: Google’s understanding of your brand, ChatGPT’s answers, HubSpot’s attribution data.
So, if your company doesn’t have a page yet, you’re effectively invisible to an entire layer of online discovery.